Data reigns as the currency of innovation, and it is precious. In the multifaceted world of technology, mastering data engineering skills has become essential to support the multi-billion dollar technology ecosystem. This sophisticated skill involves creating and maintaining data infrastructure that can process vast amounts of information with high reliability and efficiency.
As businesses push the boundaries of innovation, the role of data engineers has become more important than ever. They design systems that authenticate the smooth flow of data, optimize performance, and provide the backbone of applications and services used by millions of people.
The health of the tech ecosystem is in the capable hands of those who develop it for a living. Its growth or collapse is all dependent on how well they handle data engineering techniques.
The backbone of modern technology
Data engineering is often the unsung hero behind the smooth functioning of modern technology. It involves the meticulous process of designing, building, and maintaining scalable data systems that can efficiently handle massive inflows and outflows of data.
These systems form the backbone of tech giants, enabling them to provide uninterrupted service to their users. Data engineering ensures that everything runs smoothly. This includes aspects of e-commerce platforms that process millions of transactions a day, social media networks that handle real-time updates, or navigation services that provide real-time traffic updates.
Building resilient infrastructure
One of the main challenges of data engineering is building a resilient infrastructure that can withstand failures and protect data integrity. A highly available environment is essential, as even minor downtime can lead to significant disruption and financial losses. Data engineers use data replication, redundancy, and disaster recovery planning techniques to create robust systems.
By implementing massively parallel processing (MPP) architecture databases such as IBM Netezza and Amazon Web Services (AWS), Redshift has redefined the way enterprises handle large-scale data operations, delivering high-speed processing and reliability.
Leveraging massively parallel processing (MPP) databases
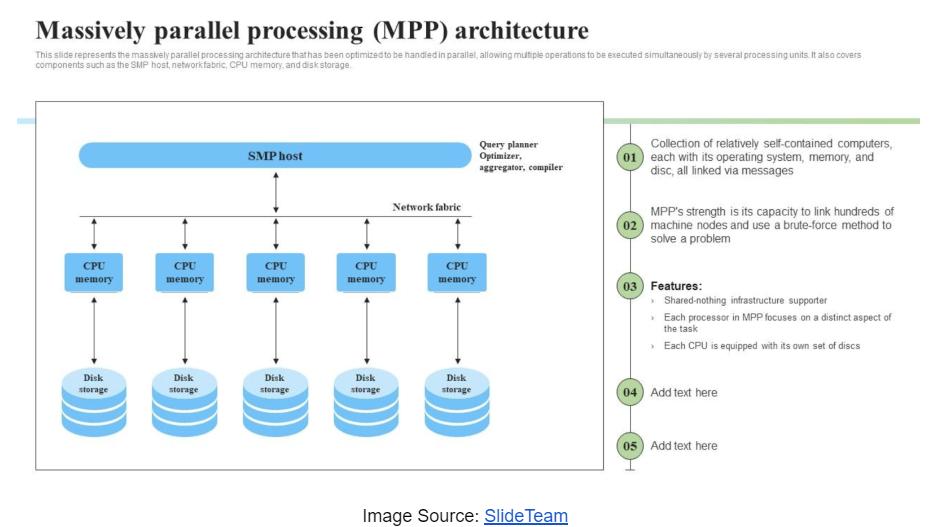

An MPP database is a group of servers that work together as a single entity. The first important component of an MPP database is how data is stored across all nodes in the cluster. The data set is divided into several segments and distributed across nodes based on the table’s distribution key. While it may be intuitive to split data equally across all nodes to utilize all resources in response to user queries, there are implications beyond just storing it for performance. There are also data skews and process skews.
Data skew occurs when data is distributed unevenly across nodes. This means that nodes carrying more data do more work than nodes carrying less data for the same user request. The slowest node in a cluster always determines the cumulative response time of the cluster. Process skew also involves uneven distribution of data across nodes. The difference in this situation is that users are only interested in data stored on some nodes. As a result, only those specific nodes are working to respond to the query usage, while other nodes are idle (i.e., underutilized cluster resources).
There is a delicate balance between how data is stored and accessed, and it must avoid data distortion and process distortion. The balance between stored and accessed data can be achieved by understanding data access patterns. Data should be shared across tables using the same unique key, which is primarily used to join data across tables. The unique key ensures uniform data distribution and ensures that tables joined with the same unique key store their data on the same node. This arrangement of data makes local data joins (co-located joins) much faster than the need to move data across nodes to produce the final data set.
Another performance improvement factor is to sort the data during the loading process. Unlike traditional databases, MPP databases do not have indexes. Instead, they eliminate unnecessary data block scans based on how the keys are sorted. You must load the data by defining a sort key, and user queries must use this sort key to avoid unnecessary data block scans.
Driving innovation through cutting-edge technology
The field of data engineering never changes, with new technologies and methodologies emerging every day to address the growing demand for data. In recent years, the adoption of hybrid cloud solutions has become a strong movement.
Enterprises can leverage cloud services such as AWS, Azure, and GCP to achieve greater flexibility, scalability, and cost efficiency. Data engineers play a critical role in evaluating these cloud offerings, determining their suitability for specific requirements, and implementing them to fine-tune performance.
Moreover, automation and artificial intelligence (AI) are revolutionizing data engineering, making processes more efficient by reducing human intervention. Data engineers are increasingly developing self-healing systems that detect problems and automatically take corrective action.
This proactive outlook reduces downtime and increases the overall reliability of your data infrastructure. Additionally, thorough telemetry monitors your system in real time to detect potential issues early and generate quick solutions.
Navigating the Digital Future: The Internet of Things and the World of People
As data volumes continue to grow tenfold, the future of data engineering promises more upgrades and challenges. Emerging technologies such as quantum computing and edge computing are poised to transform the field, providing unprecedented processing power and efficiency. Data engineers need to be able to see these trends from a mile away.
As industries move into the future at record speed, the ingenuity of data engineers will remain a key element of the digital age, powering the applications that define the Internet of Things and the human world.


